Whether your priority is saving money, helping the environment or experiencing the latest and greatest technology, electric vehicles have something for everyone.
 Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly more popular, and the demand for charging stations is growing. North Carolina's electric cooperatives, including CCEC, are working to create a statewide network of EV charging stations, enabling more consumers in both rural and urban areas to adopt this technology.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly more popular, and the demand for charging stations is growing. North Carolina's electric cooperatives, including CCEC, are working to create a statewide network of EV charging stations, enabling more consumers in both rural and urban areas to adopt this technology.
Types of Electric Vehicles
We’re most familiar with conventional combustion-engine vehicles but this list ranges from most to least amount of fossil-fuel used in operation:
- Conventional Vehicles have an internal combustion engine, the most common fuels are gasoline and diesel.
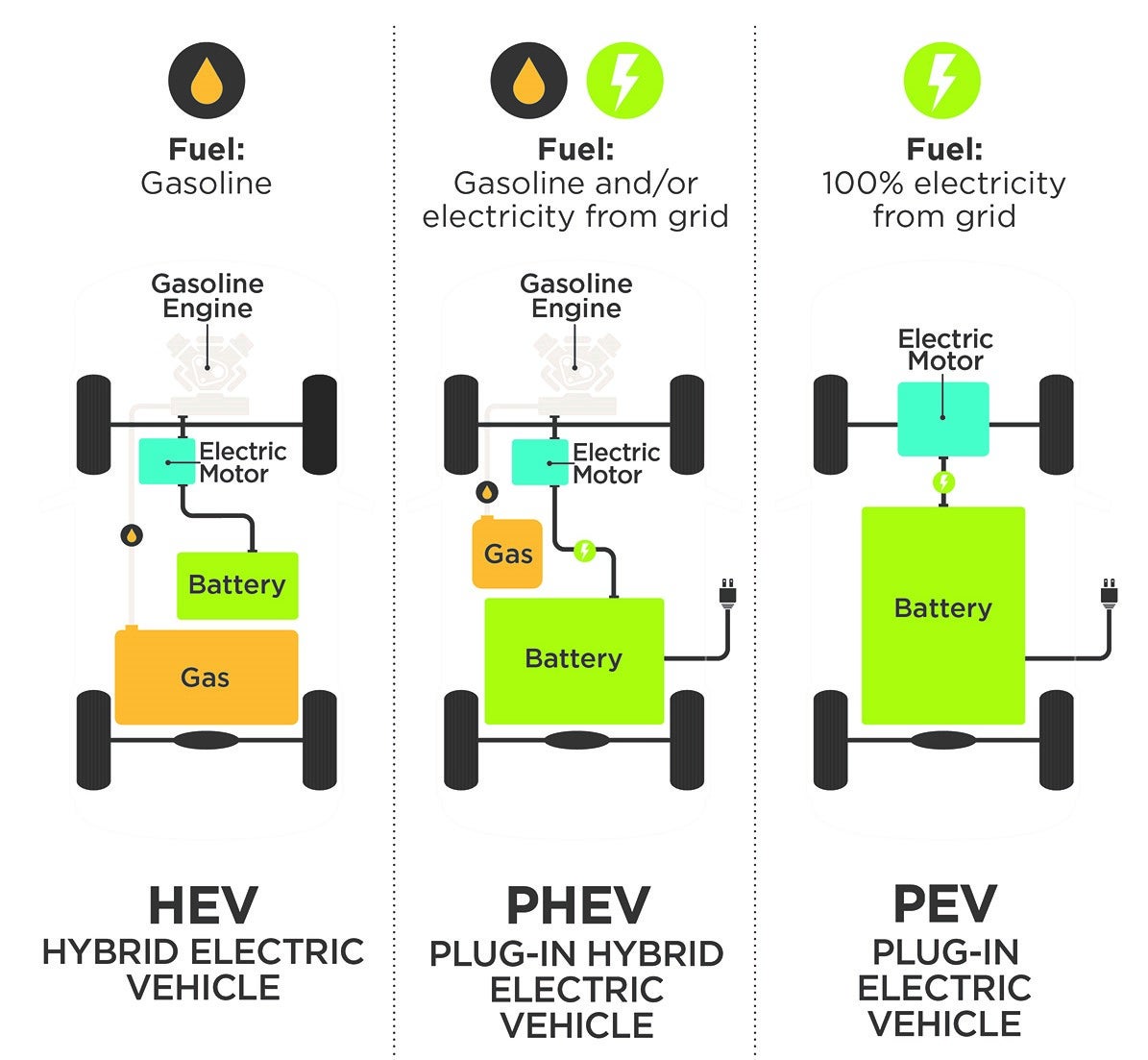
- Hybrid Vehicles (HEVs) have both a gasoline engine and an electric motor and battery; both gas and electricity power the wheels. The electric motor and battery are designed to improve fuel economy so less gasoline is used to operate the vehicle. The battery is charged solely by operating the vehicle; plug-in is not required or possible.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) have larger batteries than hybrids and use both gas and electricity to power the wheels of the car. These vehicles vary in their electric range but shift to gasoline-only operation when battery power is depleted. These vehicles must be plugged in to recharge the battery.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are powered solely by electricity and are recharged by plugging in the vehicle.
Download our Electric Vehicle 101 guide for more information.
Charging an Electric Vehicle
EV charging comes in three levels: Level 1, Level 2 and DC fast charge. Level 1 and Level 2 are common in homes, workplaces and public locations where people might visit for several hours at a time. CCEC has a Level 2 fast charger on Islander Drive in Emerald Isle.
DC Fast charging is more suited for supporting long-distance travel and is typically found along heavily trafficked corridors.
There are safety features built into electric vehicles and charging equipment. The charging cable is not live while you handle it, only when the cable is connected to the vehicle. The charger senses that the connection is properly made before the electric current is turned on. Also, the charger has a ground-fault interrupter (GFI). To prevent shocks, charging stops immediately if even a few milli-amps of current leak.
If you are considering an electric vehicle and would like a to install a home charger to your existing home or new home, be sure to read our Guide to EV-Ready Homes.
If you are a business owner that would like to install an EV charger at your place of business, download our EV-Ready Business Guide.
Seven Reasons to Go Electric
- Significant savings. Powering a car with electricity is cheaper than powering it with gas, so electric vehicles cost less to run. EVs are becoming increasing affordable to purchase, and tax incentives and rebates, can also help reduce their price tag.
- More convenience. Imagine never having to go to the gas station again! Most EV drivers charge overnight at home, and A growing network of public charging stations also make it increasingly convenient to charge your EV no matter where you’re headed.
- Less maintenance. Because EVs tend to have fewer moving parts than gasoline-powered vehicles, they require no oil changes and less maintenance, which can help you save both time and money.
- A better driving experience. Electric vehicles are fun to drive, with faster acceleration and a more responsive, zippy feel behind the wheel that offers faster pickup and improved turning power. They are quieter than gasoline-powered cars, too.
- A healthier environment. Plug-in electric vehicles have zero tailpipe emissions, which improves air quality and benefits us all. Even when accounting for generation of the electricity that powers EVs, emissions are lower than those of traditional vehicles.
- A stronger local economy. Electric vehicles decrease our dependence on foreign oil and encourage local tourism and economic development. The installation of charging stations can help promote tourism and commerce as EV drivers are drawn to the communities surrounding the stations.
- A more efficient electric grid. By charging overnight, electric vehicles create demand for power at a time when the grid has historically been most underutilized and therefore least efficient. Electricity is most expensive when demand is highest, and spreading demand across more hours of the day helps flatten those expensive peaks.

